EN 1993‑1‑1
Generally, members subject to axial compression forces and bending should be verified for cross section resistance (BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9) and for member buckling resistance (BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.3.3.(4)).
The relevant parameters required to evaluate the interaction equations given in the above clauses are presented in tabular form.
The tables are applicable to members subject to combined tension and bending and to members subject to combined compression and bending. However, the values in the tables are conservative for tension, as the more onerous compression section classification limits have been used for calculating resistances to axial force.
Tables are given for cross-section resistances and for member buckling resistances, as explained below.
6.2.9
10.1 Axial force and bending: UB sections, UC sections and parallel flange channels
10.1.1 Cross section resistance check
6.2.1(7)
For Class 1,2 and 3 cross sections the following conservative approximation may be used:
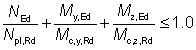 |
Eq (6.2) |
Values of Npl,Rd, Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd are given in the tables. The section classification depends on the axial force applied and therefore Mc,Rd values are given for different values of NEd/Npl,Rd. The values of these resistances have been calculated as given in the following sections.
No values are given for combined axial force and bending on Class 4 sections. Refer to BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9.3(2).
(a) Design resistance for axial force
Npl,Rd = 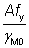 |
Eq (6.6) |
where:
| A |
is the gross area of the cross section |
| fy |
is the yield strength |
| γM0 |
is the partial factor for cross sections (γM0 = 1.0 as given in the National Annex). |
(b) Design resistances for bending about the principal axes of the cross section
6.2.5 (2)
The design resistances for bending about the major and minor axes, Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd have been calculated as in Section 8.1 using Wpl,y, Wel,y, Wpl,z and Wel,z as appropriate. No values are given for the reduced resistances in the presence of high shear.
Mc,Rd values for Class 4 cross sections are not given in the tables. For checks of Class 4 cross sections, see BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9.3(2).
The symbol X indicates that the section is Class 4 for a given value of NEd/Npl,Rd.
The symbol $ indicates that the section is Class 4 and that it would be overloaded due to compressive axial force alone i.e. the section is Class 4 and Ned > Aeff fy for the given value of NEd / Npl,Rd.
5.5.2 (8)
The Class 2 and Class 3 limits for the section subject to bending and compression are the maximum values of NEd / Npl,Rd up to which the section is either Class 2 or Class 3 respectively. The Class 2 limit is given in bold type.
6.2.9.1(2)
As an alternative to Equation (6.2) for Class 1 and 2 sections a less conservative criterion may be used as follows:
Values of MN,Rd are given in the tables.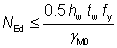
(c) Design moment resistance about the y-y axis reduced due to axial force
The reduced moment resistance MN,y,Rd has been calculated as follows:
(i) Where both the following criteria are satisfied:
NEd ≤ 0.25 Npl,Rd and 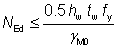 |
Eq (6.33 and 6.34) |
6.2.9.1(4)
where:
| hw |
is the clear web depth between flanges = h – 2tf |
| γM0 |
is a partial factor (γM0 = 1.0 as given in the National Annex). |
The reduced design moment resistance is equal to the plastic resistance moment
MN,y,Rd = Mpl,y,Rd
6.2.9.1(5)
(ii) Where the above criteria are not satisfied the reduced design moment resistance is given by:
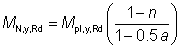 but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd |
Eq (6.36) |
where:
| Mpl,y,Rd |
is the plastic resistance moment about the y-y axis |
| n |
is the ratio NEd / Npl,Rd |
| a |
= (A – 2 b tf ) / A but ≤ 0.5. |
(d) Design moment resistance about the z-z axis reduced due to axial force
The reduced moment resistance MN,z,Rd has been calculated as follows:
6.2.9.1(4)
(i) Where the following criteria is satisfied:
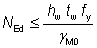 |
Eq (6.35) |
where:
| hw |
is the clear web depth between flanges = h – 2tf |
| γM0 |
is the partial factor for cross sections (γM0 = 1.0 as given in the National Annex) |
In this case, no allowance has been made for the effect of the axial force on the plastic resistance moment about the z-z axis and the reduced design moment resistance in this case is equal to the plastic resistance moment
6.2.9.1(5)
(ii) Where the above criterion is not satisfied the reduced design moment resistance is given by:
| For n ≤ a |
MN,y,Rd = Mpl,y,Rd |
Eq (6.37) |
6.2.9.5
| For n > a |
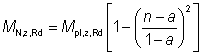 |
but ≤ Mpl,z,Rd |
Eq (6.38) |
where:
| Mpl,z,Rd |
is the plastic resistance moment about the z-z axis |
| n |
is the ratio NEd / Npl,Rd |
| a |
is as given in (c) |
Because the values of MN,y,Rd and MN,z,Rd are only valid for Class 1 and Class 2 sections, no values are shown when NEd / Npl,Rd exceeds the limit for a Class 2 section (shown as
the symbol '–' in the tables).
Reduced design moment resistances for parallel flange channels are not presented in the tables. This is because BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9 does not specifically cover the requirements for parallel flange channels.
10.1.2 Member buckling check
Interaction equations (6.61) and (6.62) from BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.3.3(4) must be satisfied for members subject to combined axial compression and bending. To check these interaction equations the following parameters given in (a), (b) and (c) are needed:
(a)
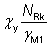
and
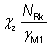
These are given in the tables as Nb,y,Rd and Nb,z,Rd. They are the compression resistances for buckling about the y-y and the z-z axis respectively. The adjacent NEd / Npl,Rd limit ensures that the section is not Class 4 and has been calculated as in Section 6.1.
(b)
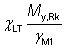
This term is given in the tables as Mb,Rd. Values are given for two NEd / Npl,Rd limits. The higher limit indicates when the section is Class 3 and the lower limit (in bold) indicates when the section is Class 2. Mb,Rd is calculated accordingly, as described in Section 8.1. In both cases it is conservatively assumed that C1 = 1.0.
(c)
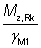
Mz,Rk may be based on the elastic or plastic modulus, depending on the section classification, as shown in Table 6.7 of BS EN 1993-1-1. Values of fyWel,z are given. Values of fyWpl,z are given as Mc,z,Rd in the tables for cross section resistance check. Values are quoted with γM1 = 1.0, as given in the National Annex.
In addition, values of fyWel,y and Npl,Rd are given in the tables for completeness.
According to the National Annex, either Annex A or Annex B of BS EN 1993-1-1 should be used to calculate the interaction factors k for UB and UC. Annex B of BS EN 1993-1-1 should be used to calculate the interaction factors k for parallel flange channels
The symbol * denotes that the cross section is Class 4 under axial compression only (due to the web becoming Class 4). None of the sections listed are Class 4 due to the flanges being Class 4. Under combined axial compression and bending, the class of the cross section depends on the axial force, expressed in terms of n (= NEd/Npl,Rd). Values of n are given, up to which the cross section would be Class 2 or Class 3.
The limits in normal and bold type are the maximum values up to which the section is either Class 3 or Class 2, respectively. The tabulated resistances are only valid up to the given NEd / Npl,Rd limit.
10.2 Axial force and bending: hollow sections
10.2.1 Cross section resistance check
6.2.1(7)
For Class 1, 2 and 3 cross sections the following conservative approximation may be used:
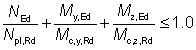 |
Eq (6.2) |
For CHS, SHS and RHS, values of Npl,Rd, Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd are given in the tables. The section classification depends on the axial force applied and therefore Mc,Rd values are given for different values of NEd/Npl,Rd. The values of these resistances have been calculated as described in the following sections.
No Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd values are given for combined axial force and bending on Class 4 sections. Refer to BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9.3(2).
The symbol * denotes that the section is Class 4 when fully stressed under axial compression only.
For elliptical hollow sections, values of Npl,Rd, Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd are given in the tables.
If an elliptical hollow section is Class 4, the design compression and bending resistances are calculated based on the area and section modulus appropriate for a Class 3 section, using a reduced design strength such that the section is Class 3. The reduced design strength is calculated using the expression given in Section 6.2(b).
(a) Design resistance for axial force
Npl,Rd =
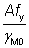
where:
| A |
is the gross area of the cross section |
| fy |
is the yield strength |
| γM0 |
is the partial factor for cross sections (γM0 = 1.0 as given in the National Annex). |
It should be noted that Npl,Rd for a class 4 elliptical hollow section is based on the gross area and a reduced design strength, as described above.
(b) Design resistances for bending about the principal axes of the cross section
6.2.5 (2)
The design resistances for bending about the major and minor axes, Mc,Rd (for CHS and SHS), Mc,y,Rd and Mc,z,Rd (for RHS and elliptical hollow sections) have been calculated as in Section 8.1 using Wpl,y, Wel,y and Wpl,z and Wel,z as appropriate. No values are given for the reduced resistance in the presence of high shear.
Mc,Rd values for Class 4 cross sections are not given in the tables. For checks of Class 4 cross sections, see BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.2.9.3(2).
If an elliptical hollow section is Class 4, the design resistances are calculated based on the section modulus appropriate for a Class 3 section and a reduced design strength such that the section is Class 3. When subject to combined axial compression and bending, elliptical hollow sections are classified for axial compression, which may be more onerous than major axis bending.
The symbol X indicates that the section is Class 4 for a given value of NEd/Npl,Rd.
The symbol $ indicates that the section is Class 4 and that it would be overloaded due to compressive axial force alone i.e. the section is Class 4 and for the given value of NEd / Npl,Rd.
5.5.2 (8)
The Class 2 and Class 3 limits for the section subject to bending and compression are the maximum values of NEd / Npl,Rd up to which the section is either Class 2 or Class 3, respectively. The Class 2 limit is given in bold type.
Limits are not given for elliptical hollow sections; the classification depends purely on the geometry of the section.
6.2.9.1(2)
As an alternative to Equation (6.2) for Class 1 and 2 CHS, SHS and RHS sections a less conservative criterion may be used as follows:
Values of MN,Rd are given in the tables.
(c) Design moment resistance reduced due to axial force
The reduced design resistances for bending have been calculated as follows:
6.2.9.1(6)
(i) Circular hollow sections
For bending about the y-y axis
where:
6.2.9.1(5)
(ii) Rectangular and square hollow sections
For bending about the y-y axis
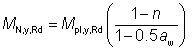 but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd |
Eq (6.39) |
where:
| aw |
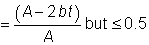 |
| Mpl,y,Rd |
is the plastic resistance moment about the y-y axis |
| n |
is the ratio NEd / Npl,Rd. |
Because the values of MN,y,Rd are only valid for Class 1 and Class 2 sections, no values are shown when NEd / Npl,Rd exceeds the limit for a Class 2 section (shown as the symbol ' – ' in the tables).
For square hollow sections, the reduced moment resistance is the same for both axes, and is displayed as MN,Rd.
6.2.9.1(5)
For bending about the z-z axis
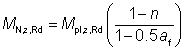 but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd |
Eq (6.40) |
where:
| af |
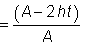 but ≤ 0.5 but ≤ 0.5 |
| Mpl,z,Rd |
is the plastic resistance moment about the z-z axis |
| n |
is the ratio NEd / Npl,Rd |
Because the values of M N,z,Rd are only valid for Class 1 and Class 2 sections, no values are shown when NEd / Npl,Rd exceeds the limit for a Class 2 section (shown as the symbol '–' in tables).
10.2.2 Member buckling check
Interaction equations (6.61) and (6.62) from BS EN 1993-1-1, 6.3.3(4) must be satisfied for members subject to combined axial compression and bending. To check these interaction equations the following parameters given in (a), (b) and (c) are needed:
(a)
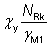
and
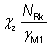
These are given in the tables as Nb,y,Rd and Nb,z,Rd for rectangular hollow sections and elliptical hollow sections, and as Nb,Rd for circular and square hollow sections. They are the compression resistances for buckling about the y-y and the z-z axis respectively. For CHS, SHS and RHS, the adjacent n limit (i.e. NEd / Npl,Rd) ensures that the section is not Class 4 and has been calculated as in Section 6.1. For Class 4 elliptical hollow sections, the design compression is calculated based on the gross area, using a reduced design strength such that the section is Class 3
When subject to combined axial compression and bending, elliptical hollow sections are classified for axial compression, which may be more onerous than major axis bending.
(b)
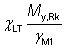
This term is given in the table as Mb,Rd for rectangular and elliptical hollow sections. For rectangular hollow sections, values are given for two NEd./ Npl,Rd limits. The higher limit ensures the section is Class 3 and the lower limit (in bold) ensures the section is Class 2, Mb,Rd is calculated accordingly. See Section 8.1. For circular and square hollow sections, this term is not applicable and is therefore not given in the tables.
(c)
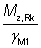
Mz,Rk may be based on the elastic or plastic modulus, depending on the section classification, as shown in Table 6.7 of BS EN 1993-1-1. Values of fyWel,z are given (for Class 4 elliptical hollow sections, a reduced value of fy is used with the elastic modulus). Values of fyWpl,z are given as Mc,z,Rd (Mc,Rd for CHS) in the tables for cross section resistance check. Values are quoted with γM1 = 1.0, as given in the National Annex.
In addition, values of fyWel,y and Npl,Rd are given in the tables for completeness.
According to the National Annex, Annex A of BS EN 1993-1-1 should be used to calculate the interaction factors k for circular, square and rectangular hollow sections.
For CHS, SHS and RHS, the symbol * denotes that the cross section is Class 4 under axial compression only (due to the web becoming Class 4). Under combined axial compression and bending, the class of the cross section depends on the axial force, expressed in terms of n (= NEd / Npl,Rd). Values of n are given, up to which the cross sections would be Class 2 or Class 3.
The limits in normal and bold type are the maximum values up to which the section is either Class 3 or Class 2, respectively. The tabulated resistances are only valid up to the given NEd / Npl,Rd limit.
For certain rectangular hollow sections, webs and flanges are Class 4. In these cases section resistances provided are based on effective section properties. These sections are indicated by the ♦ symbol.




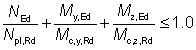
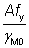
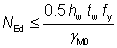
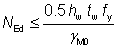
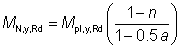 but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd
but ≤ Mpl,y,Rd 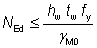
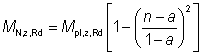
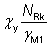 and
and 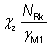
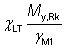
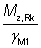
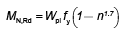
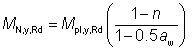 but
but 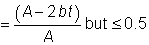
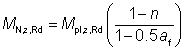 but
but 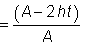 but ≤ 0.5
but ≤ 0.5